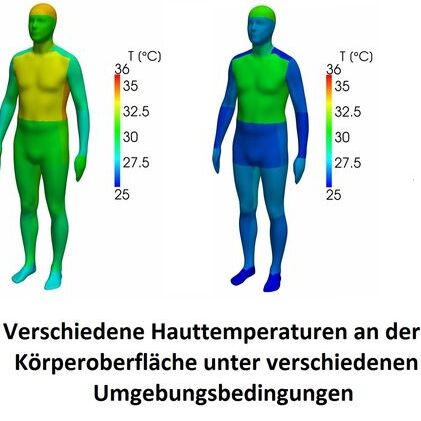
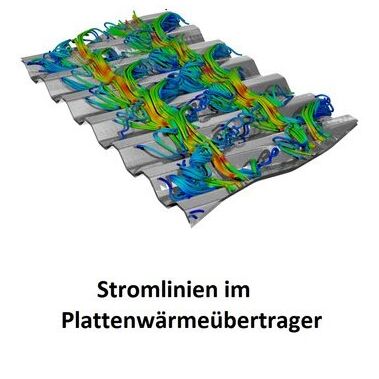
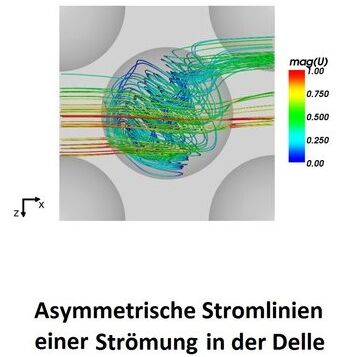
Video from Dr.-Ing. Sina Samarbakhsh
Collision of two vortex rings in frictionless flow
Due to self-induction, the rings move towards each other. Due to the mutual influence, they grow. In frictionless flow, this process continues until convective instability destroys the vortices. The motion is modeled using the finite volume method (OpenFOAM) and the computational vortex element method (CVM). The inviscid CVM reproduces this process for a longer time. The numerical diffusion in FVM transforms the two vortices into single ones. The numerical diffusion FVM is too high.
Computations by Mehrdad Kazemi
LES calculation of the plate under the angle of attack of 18 deg. Vortex structures detected by the Q-criterion and colored by mean velocity.
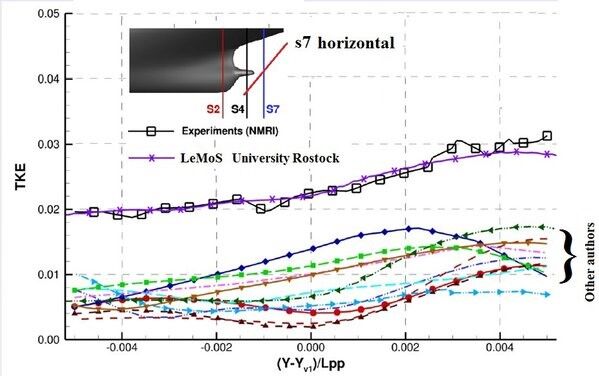
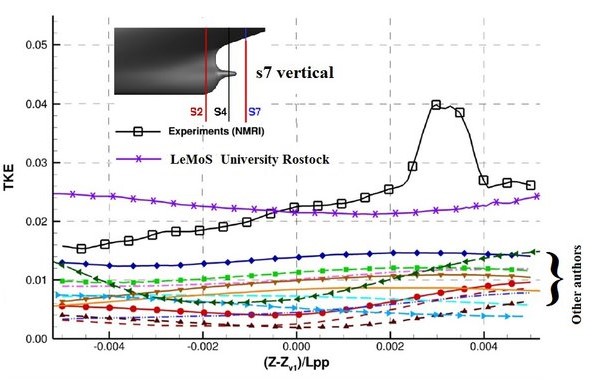
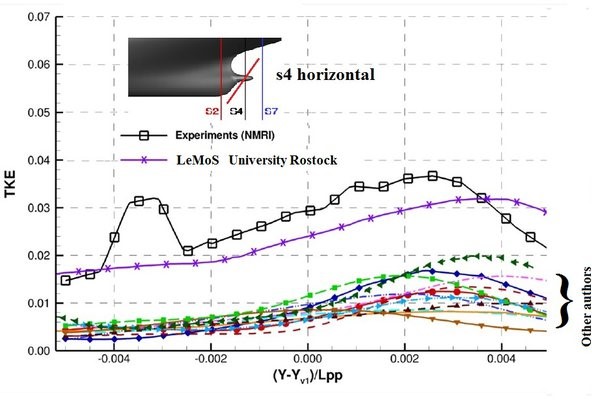
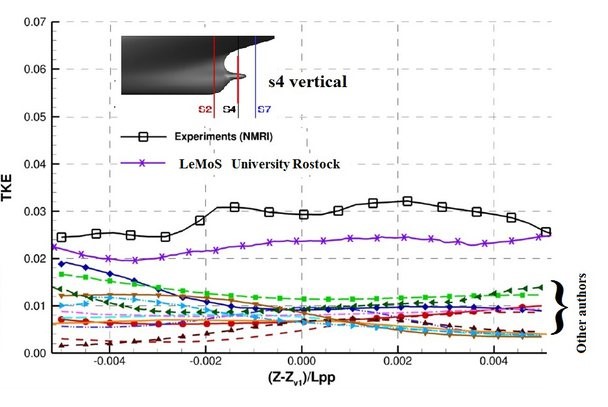
Results of prediction of the turbulent kinetic energy by different research organisations
Papers
Results were presented during the Tokyo 2015 Workshop on CFD in Ship Hydrodynamics. Different cross sections S4 and S7 behind JBC test case ship. Lines along which the distributions are presented are shown on each picture. LeMoS results were obtained using the method described in papers:
LEAPFROG Movement of two ring whorls
The LEAPFROG motion is modeled with the Finite Volume Method (OpenFOAM) and the Computational Vortex Element Method (CVM). In frictionless flow, the leafprog motion runs until convective instability destroys the vortex. One vortex passes through the next, whose radius decreases while the velocity increases. The radius of the next vortex increases and the velocity decreases. The first ring moves through the second. The process is then repeated. The inviscid CVM reproduces this process over a long period of time. Numerical diffusion in FVM transforms the two vortices into single ones. Increasing the resolution and decreasing the physical viscosity did not improve the situation. The numerical diffusion FVM is too high.